Introduction: Why Vitamin E Gummies Are Trending
Vitamin E gummies have become one of the most popular beauty supplements in the U.S., especially among those seeking radiant skin and anti-aging benefits without swallowing capsules. TikTok beauty creators and wellness influencers often call them “the glow vitamin,” claiming visible improvements in skin texture and hydration.
But the real question remains — do vitamin E gummies actually work, or are they just another overhyped trend?
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), over 90% of Americans do not get adequate vitamin E from food, driving the rise of supplementation through gummies and fortified foods.

The Science Behind Vitamin E and Skin Health
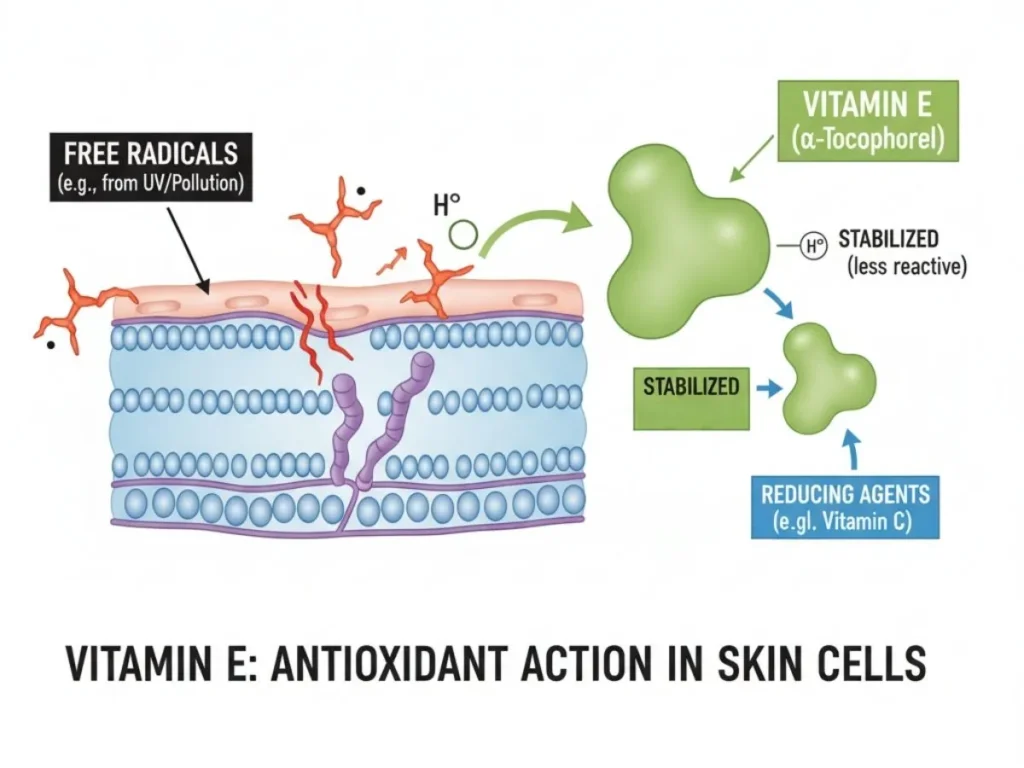
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant that protects cell membranes from oxidative damage caused by free radicals — unstable molecules that contribute to skin aging, inflammation, and UV damage.
When consumed, vitamin E integrates into cell membranes, helping maintain skin barrier function, moisture retention, and elasticity. It’s also vital for immune regulation and anti-inflammatory response.
Stat: A 2024 review published in Nutrients Journal found that regular vitamin E intake improved skin elasticity by 12–16% and reduced visible wrinkles when paired with vitamin C.
How Vitamin E Gummies Claim to Work
Vitamin E gummies are designed to deliver the nutrient in a tasty, chewable form, typically using vitamin E acetate or d-alpha-tocopherol as the active ingredient.
Many brands also combine vitamin E with other compounds like collagen, hyaluronic acid, or biotin, marketing them as “complete skin nutrition” supplements.
However, absorption varies: vitamin E requires fat for proper absorption, meaning gummies taken without a meal may offer less benefit.
Benefits Backed by Research
Clinical and observational research supports certain benefits of adequate vitamin E intake:
| Benefit | Evidence Summary | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Skin hydration & elasticity | Improved moisture retention and reduced dryness | Nutrients Journal, 2024 |
| UV protection | Helps reduce oxidative damage from sun exposure | Journal of Dermatological Science, 2023 |
| Anti-aging support | Reduces oxidative stress that leads to wrinkles | American Journal of Clinical Nutrition |
| Immune function | Supports immune cell defense and repair | NIH Office of Dietary Supplements |
Expert Insight:
“Topical vitamin E often works best when paired with oral intake, creating a dual antioxidant defense that enhances barrier repair,” explains Dr. Laura Wexler, Dermatologist, New York Skin Institute.
Potential Downsides and Safety Concerns
While vitamin E gummies are generally safe, over-supplementation can be problematic.
- High doses (above 400 IU daily) may increase bleeding risk, especially for individuals on blood thinners.
- Artificial sugars or gelatin in some gummies can cause bloating or digestive discomfort.
- Synthetic forms (dl-alpha-tocopherol) may be less bioavailable than natural d-alpha-tocopherol.
The NIH recommends keeping total daily intake below 1000 mg (1500 IU) for adults.
Who Actually Needs Vitamin E Supplementation?
Most Americans can meet vitamin E needs through food, but supplementation may help if you:
- Follow low-fat or restricted diets (since vitamin E is fat-soluble)
- Have digestive disorders like Crohn’s disease or celiac disease
- Are exposed to high oxidative stress (pollution, smoking, intense workouts)
- Experience dry skin or early signs of aging
For healthy adults, the recommended daily allowance (RDA) is 15 mg (22.4 IU).
Natural Sources of Vitamin E
Food remains the most bioavailable and balanced source of vitamin E:
| Food Source | Serving Size | Vitamin E (mg) |
|---|---|---|
| Sunflower seeds | 1 oz | 7.4 |
| Almonds | 1 oz | 6.8 |
| Avocado | 1 medium | 4.2 |
| Spinach (cooked) | 1 cup | 3.7 |
| Olive oil | 1 tbsp | 1.9 |

Actionable Checklist: Maximizing Vitamin E Benefits
☑ Pair vitamin E gummies with a meal containing healthy fats.
☑ Choose products using natural d-alpha-tocopherol instead of synthetic versions.
☑ Avoid gummies with excessive sugar or artificial coloring.
☑ Rotate between whole food and supplement sources.
☑ Consult a healthcare provider if taking blood thinners or supplements exceeding 400 IU/day.
Expert Insights
“Vitamin E supplementation benefits those with low intake, but real, lasting improvements in skin health come from balanced nutrition — not just gummies,” says Dr. Michelle Harper, Clinical Nutritionist, Los Angeles.
“Combining vitamin E with antioxidants like vitamin C and selenium offers synergistic effects for cellular protection,” adds Dr. Jason Turner, Functional Medicine Expert.
Common Myths & FAQ
Q1: Can I take vitamin E gummies daily?
Yes, but stay within 15–30 mg (22–45 IU) unless medically advised for higher doses.
Q2: Are vitamin E gummies as effective as capsules?
They can be, provided they contain natural tocopherol and are taken with fats.
Q3: Will vitamin E gummies clear acne?
Not directly. While vitamin E supports barrier repair, acne is more complex and often hormonal or bacterial.
Q4: How long before results appear?
Visible skin improvements generally take 6–8 weeks of consistent intake.
Authoritative Resources
- NIH Office of Dietary Supplements – Vitamin E Fact Sheet
- American Academy of Dermatology – Antioxidants and Skin Health
- The Nutrition Source – Vitamin E
Other Interesting Articles
- The Forgotten Mineral: Why Americans Are Chronically Low in Boron
- Post-Workout Carb Confusion: How to Refuel Without Storing Fat
Conclusion & Call-to-Action
Vitamin E gummies can support healthy, glowing skin — but they work best as part of a nutrient-rich, antioxidant-balanced diet.
They’re not miracle cures but useful tools for individuals with low intake or specific needs.
To see real benefits, prioritize whole food sources, avoid sugar-loaded supplements, and pair vitamin E with complementary nutrients like vitamin C and omega-3 fats.
Next Step: Choose a clean, third-party tested vitamin E gummy and start tracking your results over 6–8 weeks.

