Introduction: What is Thermal Contrast Therapy?
Thermal contrast therapy involves alternating hot and cold exposure to stimulate physiological adaptation. Traditionally rooted in Scandinavian and Eastern practices, this therapy has gained mainstream attention in the U.S. wellness community, including elite athletes, biohackers, and fitness enthusiasts.
By strategically alternating between sauna or hot baths and cold plunges or ice baths, thermal contrast therapy can improve immune function, mood, circulation, and recovery.
📊 Statistic: A 2023 study in Frontiers in Physiology found participants practicing regular thermal contrast therapy had 25% higher markers of immune resilience compared to controls.

The Science Behind Hot & Cold Exposure
Human physiology responds to thermal stress through:
- Vasodilation & Vasoconstriction: Hot exposure dilates blood vessels, increasing circulation, while cold exposure constricts vessels, reducing inflammation.
- Hormonal Response: Thermal contrast stimulates endorphins, norepinephrine, and cortisol regulation, improving mood and stress tolerance.
- Immune Activation: Cold exposure can increase white blood cell count and cytokine response, supporting infection defense.
Expert Quote:
“Alternating heat and cold stresses the body in a controlled way, enhancing recovery, immune resilience, and mental clarity,” says Dr. Laura Michaels, MD, Integrative Medicine Specialist.
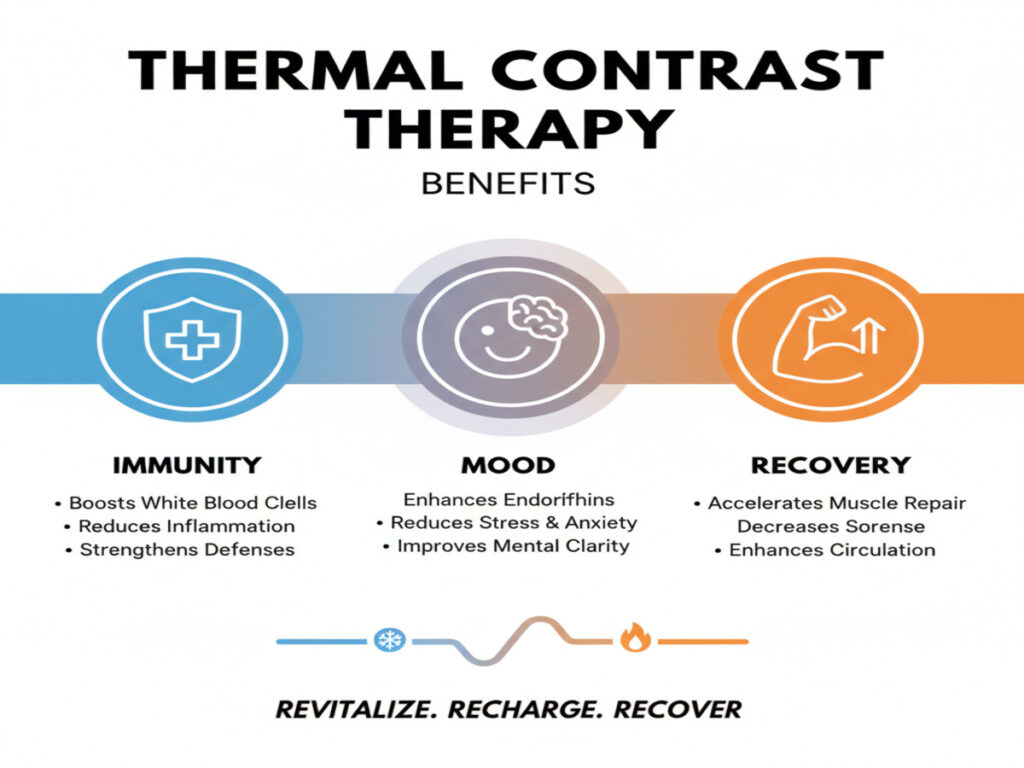
Benefits of Thermal Contrast Therapy
Immune System Support
- Enhances circulation and lymphatic flow
- Boosts natural killer cell activity
- Reduces chronic inflammation markers
Mood Enhancement & Mental Health
- Increases endorphins and dopamine release
- Reduces perceived stress and anxiety
- Improves sleep quality
Physical Recovery & Performance
- Accelerates muscle recovery post-exercise
- Reduces delayed-onset muscle soreness (DOMS)
- Improves joint mobility and circulation
📊 Statistic: Research in Journal of Athletic Training (2022) shows athletes using hot/cold contrast therapy experienced 30% faster muscle recovery.
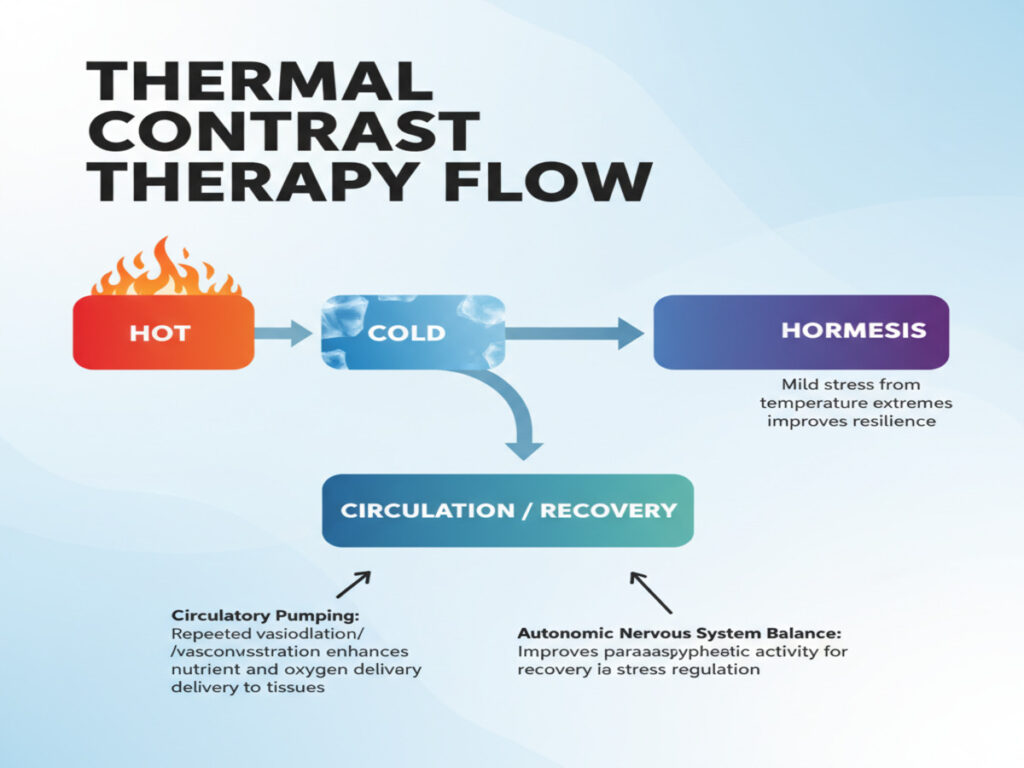
How Thermal Contrast Therapy Works
Thermal contrast works by alternating hot and cold stimuli to trigger adaptive physiological responses. Key mechanisms include:
- Hormesis: Mild stress from temperature extremes improves resilience.
- Circulatory Pumping: Repeated vasodilation/vasoconstriction enhances nutrient and oxygen delivery to tissues.
- Autonomic Nervous System Balance: Improves parasympathetic activity for recovery and stress regulation.
Types of Thermal Contrast Protocols
| Protocol | Description | Recommended Users |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Sauna + Ice Bath | 10-15 min sauna, 1-3 min cold plunge | Fitness enthusiasts & biohackers |
| Hot Shower + Cold Rinse | 5-10 min hot, 30-60 sec cold rinse | Beginners & home users |
| Contrast Hydrotherapy | Alternate hot/cold pools for 3-5 cycles | Spa or professional recovery |
| Dry Sauna + Cold Plunge | Sauna 15-20 min, cold plunge 1-2 min | Advanced users for immune boost |
Actionable Daily Thermal Contrast Strategies
- Begin Gradually: Start with shorter cold exposure, longer hot sessions.
- Hydrate Well: Thermal stress increases fluid loss; drink 2-3 liters water.
- Pair with Recovery Nutrition: Protein and antioxidants post-session optimize adaptation.
- Schedule Around Workouts: Cold exposure post-training reduces soreness; sauna post-training aids relaxation.
- Consistency: Aim for 2-4 sessions per week to achieve measurable benefits.
💡 Tip: Track your heart rate and perceived exertion to ensure safe exposure.
Practical Checklist for Safe Thermal Contrast
✔ Start with short cold exposure (30–60 sec)
✔ Limit sauna sessions to 15–20 minutes initially
✔ Hydrate before, during, and after sessions
✔ Avoid alcohol prior to therapy
✔ Use non-slip surfaces to prevent accidents
✔ Listen to your body; stop if dizzy or uncomfortable
✔ Gradually increase intensity over 2–4 weeks
Thermal Exposure Comparison Table
| Exposure | Duration | Benefits | Risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sauna | 10-20 min | Circulation, detox, relaxation | Dehydration if prolonged |
| Hot Bath | 10-15 min | Relaxation, circulation | Overheating |
| Cold Plunge | 1-3 min | Immune boost, recovery | Hypothermia if excessive |
| Cold Shower | 30-90 sec | Mood, circulation | Initial shock, dizziness |
Expert Insights on Hot & Cold Therapy
- “Thermal contrast is one of the few interventions with simultaneous mental and physical benefits,” — Dr. Miguel Alvarez, Cardiologist, Mayo Clinic.
- “Cold exposure triggers norepinephrine release, improving focus and mood,” — Dr. Karen Holt, MD, Integrative Medicine Specialist.
- “The repeated vascular stress of hot/cold cycling enhances recovery and cardiovascular resilience,” — Dr. Emily Torres, Functional Medicine Specialist.
Common Myths & FAQ
Q1: Is cold exposure dangerous?
A: Safe if started gradually and limited to 1-3 minutes; avoid if you have cardiovascular disease without physician clearance.
Q2: Can thermal contrast replace exercise?
A: No, it complements exercise by improving recovery, circulation, and resilience.
Q3: Do I need a sauna to practice thermal contrast?
A: No, hot showers and cold showers can provide similar benefits for beginners.
Q4: How often should I practice thermal contrast?
A: 2–4 sessions per week are sufficient for measurable benefits.
Authoritative Resources
- Mayo Clinic – Sauna & Cold Therapy Benefits
- Harvard Health – Cold Exposure and Immunity
- NIH – Thermotherapy Research
- Frontiers in Physiology – Thermal Contrast Studies
Conclusion & Call-to-Action
Thermal contrast therapy is a powerful, evidence-based strategy for enhancing immunity, mood, and recovery. By gradually incorporating hot and cold exposure into your weekly routine, you can boost circulation, accelerate recovery, and increase mental clarity.
👉 Next Step: Begin with short hot/cold sessions, track your body’s response, and gradually build intensity. Over time, you’ll notice improved recovery, better mood, and stronger immune resilience.

