Brain fog isn’t just a feeling of mental sluggishness — it’s often the earliest sign of an underlying biological process known as neuroinflammation. In 2025, Americans are reporting record rates of fatigue, lack of focus, and mood instability — symptoms that trace back to an inflamed brain. This article breaks down what’s really happening inside your head, what’s causing it, and how to fix it naturally.
What Is Neuroinflammation?
Neuroinflammation refers to inflammation within the brain and central nervous system. Unlike typical inflammation from an injury or infection, this type occurs on a microscopic level and can quietly disrupt brain communication and energy metabolism.
When microglial cells — the brain’s immune defenders — become overactive, they start producing inflammatory molecules (cytokines and free radicals) that damage neurons and slow neurotransmission. This leads to cognitive fatigue, poor memory, anxiety, and the classic “foggy” feeling many people describe.
The Hidden Triggers Behind Brain Inflammation
Modern American lifestyles create the perfect storm for chronic low-grade brain inflammation. The biggest triggers include:
| Trigger | Description | Everyday Example |
|---|---|---|
| Poor Metabolic Health | High blood sugar and insulin resistance can inflame blood vessels in the brain. | Frequent snacking, ultra-processed carbs. |
| Chronic Stress | Elevated cortisol weakens the blood-brain barrier, allowing toxins to enter. | Constant work pressure, poor sleep. |
| Environmental Toxins | Air pollutants and pesticides trigger microglial activation. | Urban living, non-organic produce. |
| Sleep Deprivation | During deep sleep, the brain clears inflammatory waste via the glymphatic system. | Using screens late at night. |
| Gut Dysbiosis | Leaky gut allows inflammatory compounds to reach the brain. | Low-fiber diet, antibiotic overuse. |
The Science of Brain Fog and Cognitive Fatigue
Recent research from the National Institute on Aging shows that neuroinflammation reduces mitochondrial energy output in neurons, leading to a literal energy deficit in the brain.
When this happens, you can still perform basic mental tasks, but higher-level executive functions — focus, creativity, decision-making — start to deteriorate.
According to a 2024 Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience review, this mechanism is also linked to early cognitive decline and age-related neurodegeneration.
Early Signs You Might Have Neuroinflammation
If you experience several of these symptoms regularly, your brain may be inflamed — even if standard medical tests show “normal” results:
- Morning fatigue even after sleeping 7–8 hours
- Reliance on caffeine to concentrate
- Forgetfulness or word recall issues
- Irritability or low motivation
- Sensitivity to stress or noise
- Headaches or pressure behind the eyes
Actionable Strategies to Reduce Neuroinflammation Naturally
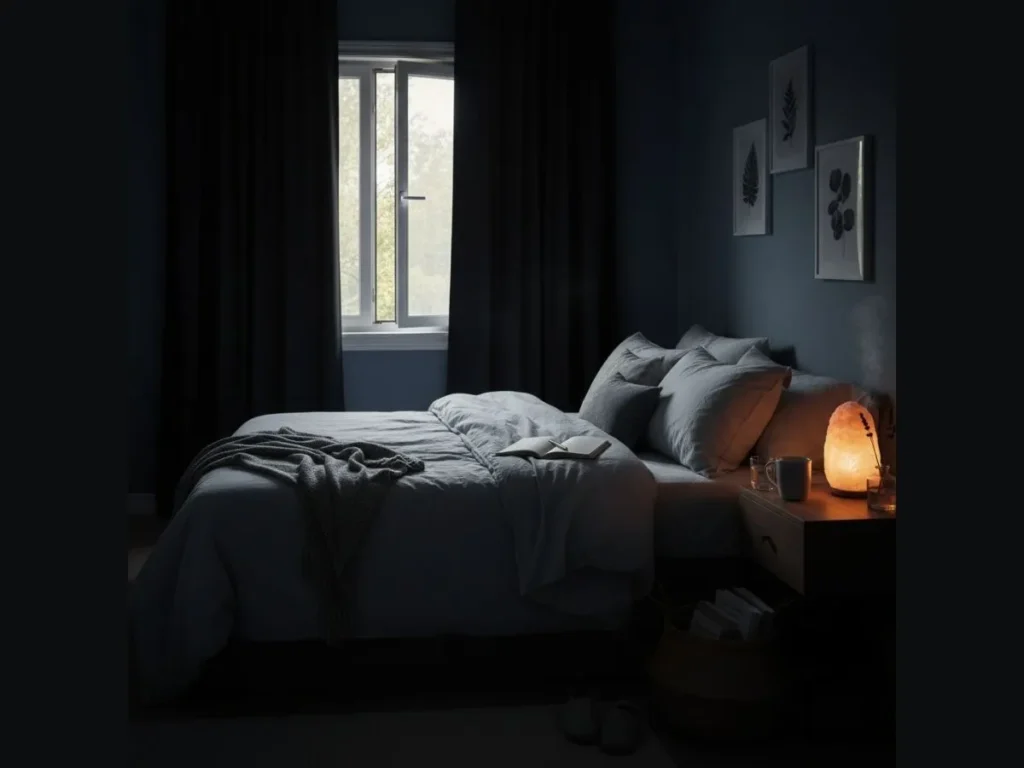
1. Prioritize Deep Sleep
The brain’s waste-clearing system (the glymphatic system) is most active during deep sleep. Maintain a dark, cool bedroom and avoid screens an hour before bed to boost melatonin.

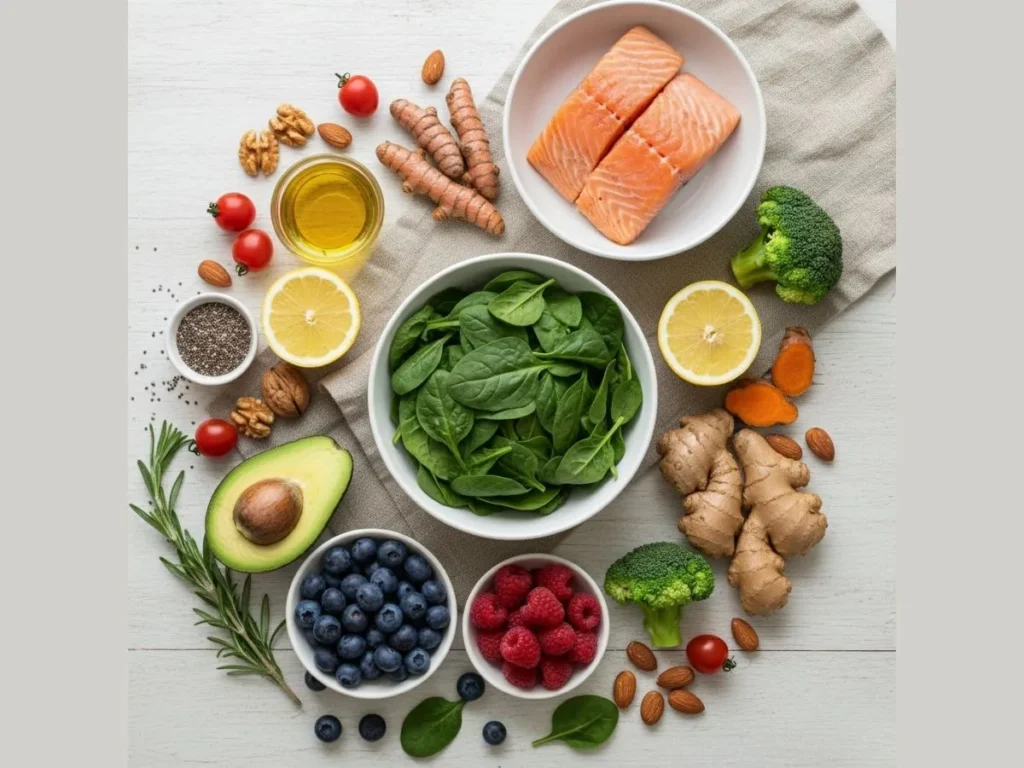
2. Adopt an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Focus on omega-3 fatty acids (salmon, flaxseed), polyphenols (berries, olive oil), and cruciferous vegetables. Limit sugar and refined oils.

3. Support the Gut-Brain Axis
Take a quality probiotic, include fermented foods, and eat high-fiber vegetables daily. A healthier gut reduces inflammatory cytokines reaching the brain.
4. Exercise Regularly (Especially Aerobic Workouts)
Aerobic training increases BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor), which helps neurons grow and recover from inflammatory stress. Even 30 minutes of brisk walking five days a week makes a measurable difference.
5. Try Natural Neuroprotective Nutrients
Emerging research supports the following compounds for reducing neuroinflammation:
| Nutrient | Function | Common Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Curcumin | Reduces inflammatory cytokines | Turmeric |
| Omega-3s (DHA/EPA) | Supports neuronal membrane health | Fatty fish, algae oil |
| Magnesium L-threonate | Enhances synaptic function | Supplements |
| Resveratrol | Protects brain mitochondria | Red grapes, supplements |
| CoQ10 | Supports neuronal energy production | Organ meats, supplements |
6. Cold Exposure and Sauna Therapy
Alternate between heat (sauna) and cold (cold showers or ice baths). This stimulates heat shock proteins and reduces systemic inflammation.
Expert Insight
“Neuroinflammation is no longer just a term for researchers. It’s the missing link in understanding why so many Americans feel exhausted and unfocused despite sleeping and eating well.”
— Dr. Dale Bredesen, Neurologist and Author of The End of Alzheimer’s
Authoritative Resources
- National Institute on Aging – Inflammation and Brain Health
- Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience – Neuroinflammation and Cognitive Decline
- Harvard Health – How Inflammation Affects Mental Clarity
Other Interesting Articles on Fitoast
- Blue Light Insomnia: How Evening Screen Use Is Quietly Destroying Sleep Hormones
- Modern Sedentary Syndrome: The New Metabolic Threat in Remote Workers
FAQ: Neuroinflammation & Brain Fog
Q1. Can neuroinflammation be reversed?
Yes, lifestyle interventions like anti-inflammatory diets, regular exercise, and quality sleep can significantly lower brain inflammation over time.
Q2. Are blood tests available to detect neuroinflammation?
Currently, most tests are indirect. Markers like CRP, IL-6, and homocysteine may indicate systemic inflammation, but neuroimaging or cerebrospinal analysis is more accurate.
Q3. Is brain fog a sign of early dementia?
Not necessarily. Brain fog is usually reversible, while dementia involves permanent structural damage.
Q4. How long does it take to feel better after addressing inflammation?
Most people report cognitive improvements within 2–6 weeks of consistent lifestyle changes.
Q5. Does caffeine worsen neuroinflammation?
In moderate amounts, caffeine can be neuroprotective. Overuse, however, can elevate stress hormones and indirectly worsen inflammation.
Conclusion
Neuroinflammation is the hidden force behind modern fatigue and cognitive decline. Fortunately, it’s reversible through targeted nutrition, stress management, and better metabolic health. By treating brain health as part of whole-body wellness, you can reclaim clarity, focus, and long-term energy — one healthy habit at a time.

