Introduction: What Is Mindful Muscle?
Mindful Muscle is the practice of integrating conscious breathing with physical training to enhance strength, endurance, and recovery. It’s not meditation in motion — it’s performance optimization through physiological awareness.
In the United States, where stress, overtraining, and sedentary habits dominate fitness culture, breath-focused training offers a grounded way to restore balance between effort and recovery. This technique blends science-backed breathing patterns with strength training to elevate both mind and muscle function.
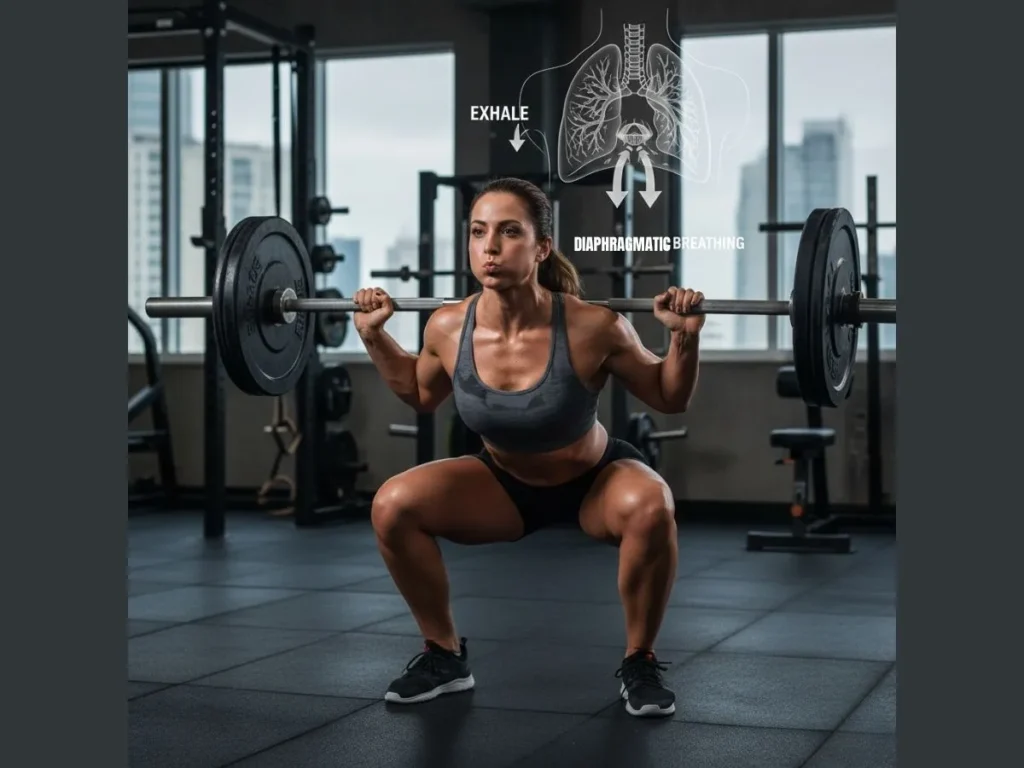

The Science Behind Breath-Focused Training
Breathing directly influences the autonomic nervous system, which regulates stress, muscle tension, and recovery.
When you train with mindful breathing:
- Inhalation activates the sympathetic system (energy & alertness).
- Exhalation engages the parasympathetic system (calm & recovery).
By controlling these phases, athletes can shift between performance intensity and recovery more efficiently.
Statistic: A 2023 University of Colorado study found that structured breathing during resistance training improved oxygen efficiency by 15% and reduced perceived exertion by 12%.
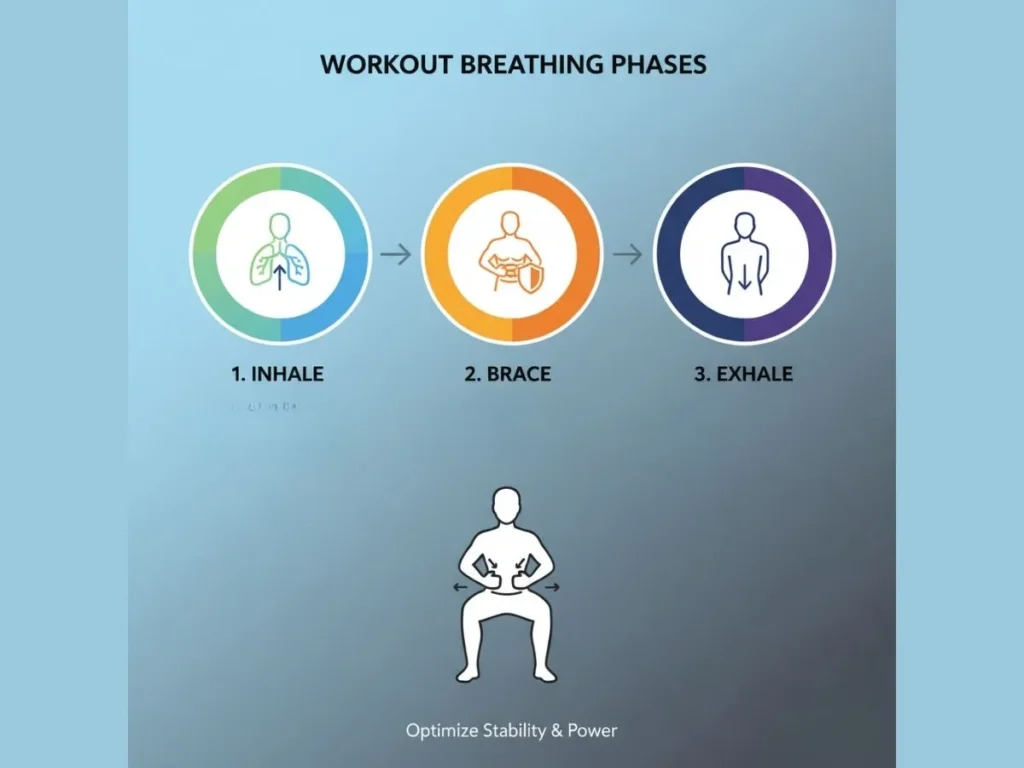
Benefits of Integrating Breath and Movement
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Core Stability | Controlled breathing activates the diaphragm and deep core muscles, enhancing lift safety and stability. |
| Improved Oxygen Utilization | Mindful breathing ensures efficient oxygen delivery to working muscles. |
| Enhanced Recovery | Regulated breathing lowers cortisol and speeds post-workout recovery. |
| Reduced Muscle Fatigue | Oxygen balance delays lactic acid buildup during high-intensity training. |
| Mental Focus | Breath awareness boosts cognitive control and workout concentration. |
How Breathing Impacts Strength, Endurance, and Recovery
- Strength: Breath bracing — also called the Valsalva maneuver — increases intra-abdominal pressure, allowing heavier and safer lifts.
- Endurance: Rhythmic breathing optimizes oxygen-carbon dioxide exchange, improving running or cycling output.
- Recovery: Slow exhalation activates the parasympathetic response, reducing heart rate and inflammation post-training.
Expert Quote:
“Breathing is not an accessory to movement; it’s the foundation of performance. When you sync your breath, you unlock your nervous system’s full potential,” — Dr. Karen Liu, Exercise Physiologist, National Strength & Conditioning Association.
Common Breathing Patterns in Fitness
| Pattern | When to Use | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Inhale during eccentric, exhale during concentric | Weight training | Stabilizes and strengthens core |
| 4-4-4-4 Box Breathing | Pre/post-workout | Reduces anxiety, improves focus |
| Nasal Breathing | Endurance training | Increases CO₂ tolerance, better oxygen use |
| Diaphragmatic Breathing | Recovery sessions | Improves lung capacity and stress response |
Actionable Mindful Muscle Techniques
- Start Every Set with Breath Awareness: Take 3 deep diaphragmatic breaths before each lift.
- Exhale with Effort: Exhale through the mouth during exertion to engage the core.
- Use Breath Pauses for Focus: Pause after inhalation to stabilize before lifting.
- Incorporate Breath Sets: Between workout sets, use 1-minute controlled breathing for better recovery.
- Mindful Cooldowns: Finish every session with 3–5 minutes of nasal breathing to reduce inflammation and heart rate.

Practical Checklist for Breath-Focused Training
✅ Warm up with 2–3 minutes of deep diaphragmatic breathing
✅ Pair every lift with intentional breath control
✅ Avoid shallow chest breathing
✅ Use nasal breathing for low-intensity cardio
✅ End sessions with relaxation breathing
✅ Track breathing rate improvements over time
Expert Insights on Mindful Training
“Mindful breathwork increases barbell efficiency, speed recovery, and reduces overtraining risks,” — Dr. Jacob Fields, Human Performance Lab, Texas A&M.
“Recovery starts the moment you exhale mindfully after your last rep. Most people miss that,” — Lindsay Scott, Certified Strength Coach (CSCS).
Common Myths & FAQ
Q1: Is mindful breathing only for yoga or meditation?
A: No. It’s a key performance enhancer in weightlifting, running, and HIIT.
Q2: Can breathwork replace recovery techniques like ice baths?
A: No, but it enhances recovery by optimizing oxygen delivery and nervous system balance.
Q3: Will it slow down high-intensity training?
A: Done right, it actually improves endurance and focus, not slows it.
Q4: How long until benefits appear?
A: Most athletes report better control and endurance in 2–3 weeks of consistent practice.
Authoritative Resources
- American Council on Exercise (ACE): Breathing & Performance
- National Strength & Conditioning Association: Role of Breathing in Exercise
- Harvard Health: The Science of Breathwork
Other Interesting Articles
Conclusion & Call-to-Action
Mindful Muscle training represents a shift from mechanical movement to intelligent performance. Breath-focused training enhances strength, endurance, and recovery by merging physiological science with awareness.
To implement this today:
- Begin every workout with 3–5 deep diaphragmatic breaths.
- Sync your breathing with your reps.
- End with slow nasal breathing to accelerate recovery.
Next step: practice intentional breathing for one week and track how your focus, strength, and recovery improve. Your performance may change more than you imagine.

