Introduction: Why Glycine Is Gaining Attention
Glycine, a non-essential amino acid, has quietly become one of the most talked-about sleep aids among fitness enthusiasts and biohackers in the U.S. It’s not a stimulant or a sedative, but rather a naturally calming compound that helps your body unwind at night.
By promoting deep sleep quality, balancing body temperature, and supporting muscle repair, glycine offers a holistic way to restore energy without dependency on sleep medications or high-dose melatonin.

The Science Behind Glycine and Sleep
Glycine acts as both an amino acid and a neurotransmitter. It works by:
- Lowering core body temperature, signaling your brain it’s time to sleep.
- Activating parasympathetic (“rest and digest”) pathways, which reduce stress.
- Enhancing serotonin and melatonin regulation, helping synchronize circadian rhythms.
Research Insight
A 2007 study published in Sleep and Biological Rhythms found that taking 3 grams of glycine before bed improved sleep efficiency and reduced fatigue in subjects with poor sleep.
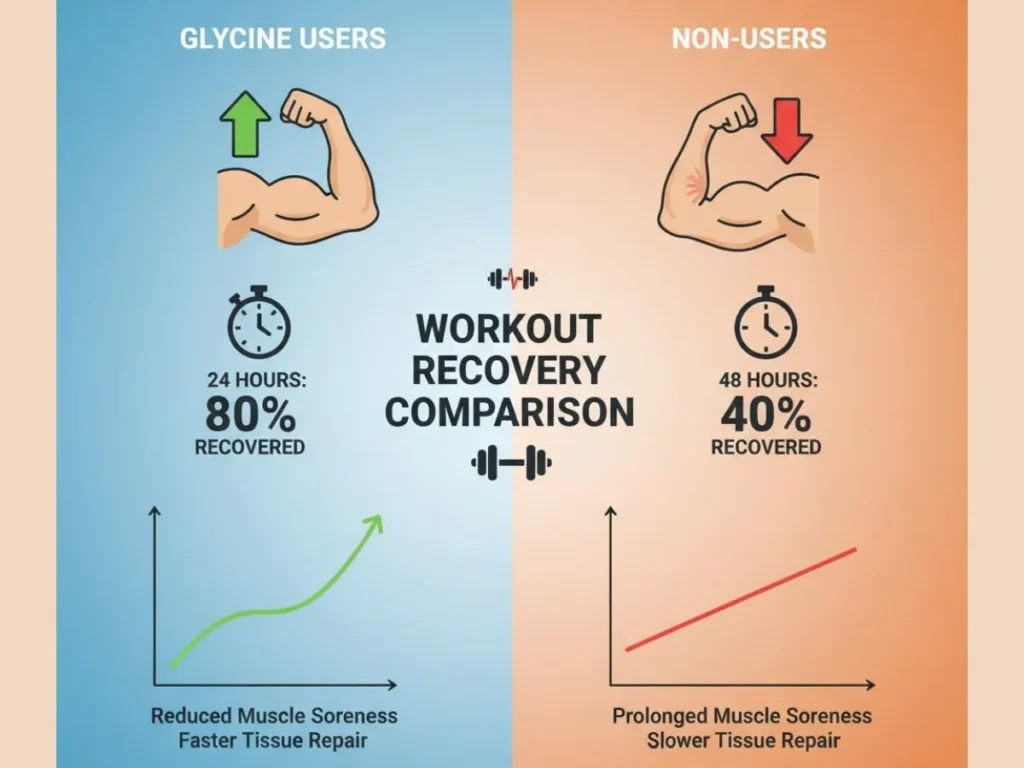
How Glycine Supports Muscle Recovery and Nervous System Balance
Beyond sleep, glycine supports muscular and neurological repair:
- Collagen synthesis: Essential for joint and muscle tissue recovery.
- Glutathione production: A master antioxidant aiding post-exercise repair.
- CNS modulation: Reduces overexcited nerves after intense training, promoting relaxation.
Athletes who struggle with nighttime rest after evening workouts may find glycine particularly beneficial.
Benefits of Taking Glycine Before Bed
| Benefit | How It Helps | Scientific Basis |
|---|---|---|
| Improves sleep onset | Helps fall asleep faster | Lowers core body temperature |
| Enhances deep sleep | Increases slow-wave sleep | Boosts serotonin and melatonin |
| Reduces fatigue | Promotes restorative rest | Enhances mitochondrial repair |
| Supports recovery | Boosts protein synthesis | Aids collagen and antioxidant activity |
| Reduces anxiety | Calms overactive neurons | Acts as an inhibitory neurotransmitter |
Dosage, Timing, and Safe Usage
- Recommended dosage: 3–5 grams of glycine, taken 30–60 minutes before bedtime.
- Form: Powder or capsules (powder dissolves easily in water or herbal tea).
- Best pairings: Magnesium glycinate or collagen peptides for synergistic benefits.
- Caution: Avoid excessive intake (>10 g/day) as it may cause mild stomach upset.
Tip: Start with 2 grams to assess tolerance before increasing dosage.

Food Sources of Glycine
| Food Source | Serving Size | Glycine Content (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| Gelatin (unflavored) | 1 tbsp | 3 g |
| Chicken skin | 3 oz | 1.7 g |
| Pork rinds | 1 oz | 1.5 g |
| Bone broth | 1 cup | 1–2 g |
| Collagen powder | 1 scoop | 2–3 g |
For most Americans, supplementing remains the most practical way to achieve consistent glycine intake.
Suggested image placement: A table showing collagen-rich foods and bone broth bowls with a “Natural Glycine Sources” heading.
Checklist: Building a Night Routine with Glycine
✅ Take glycine 30–60 minutes before sleep.
✅ Limit screen exposure and blue light 1 hour before bed.
✅ Maintain a cool, dark sleep environment (65–68°F).
✅ Combine with magnesium glycinate or chamomile tea.
✅ Keep a consistent bedtime schedule.
Expert Insights
“Glycine before bed can improve both sleep latency and sleep depth. It’s a low-risk, evidence-supported option that naturally enhances recovery,” — Dr. Alan Pierce, Clinical Nutritionist, California.
“Unlike melatonin, glycine doesn’t disrupt natural hormone rhythms. It helps reset circadian cues instead of overriding them,” — Dr. Marissa Gray, Sleep Medicine Specialist, Boston.
Common Myths & FAQ
Q1: Does glycine make you drowsy?
No. Glycine promotes relaxation, not sedation. It helps you fall asleep naturally by calming the nervous system.
Q2: Can I take glycine with other supplements?
Yes. It pairs well with magnesium, taurine, and collagen peptides for nighttime recovery.
Q3: How long before results appear?
Most people report noticeable improvements in 3–5 days of consistent use.
Q4: Is glycine safe for long-term use?
Yes. Studies show long-term supplementation (up to 90 days) is safe when dosed properly.
Authoritative Resources
- National Institutes of Health – Amino Acids and Sleep Research
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine – Nutrient-Based Sleep Strategies
- Harvard Health – Natural Ways to Improve Sleep Quality
Other Interesting Articles on Fitoast
- Cycle Syncing for Performance & Hormone Balance: Myth or Undervalued Tool?
- Silent Nutrient Pairings: The Overlooked Combinations That Supercharge Absorption
Conclusion & Call-to-Action
Glycine is one of the most underrated amino acids in modern health. It doesn’t just help you fall asleep — it helps you restore. By optimizing nervous system function, reducing inflammation, and improving recovery, it’s a true foundation nutrient for anyone chasing longevity, fitness, or simply better rest.
Next Step: Try 3 grams of glycine before bed for one week. Track your sleep quality and energy levels each morning — you may notice deeper rest, faster muscle recovery, and greater calm.

