Introduction: The Overlooked Trace Mineral
Boron — a trace mineral often left out of most nutrition discussions — plays a surprisingly critical role in human health. Despite being essential for plant growth and bone metabolism, it’s not classified as an “essential nutrient” for humans by the FDA. Yet, emerging research suggests Americans may be chronically under-consuming it.
In the U.S., the average daily boron intake is only 1–1.5 mg, well below the estimated optimal intake of 3–6 mg linked with better bone density, hormone regulation, and cognitive performance. The culprit? Over-processed diets and declining soil mineral content.

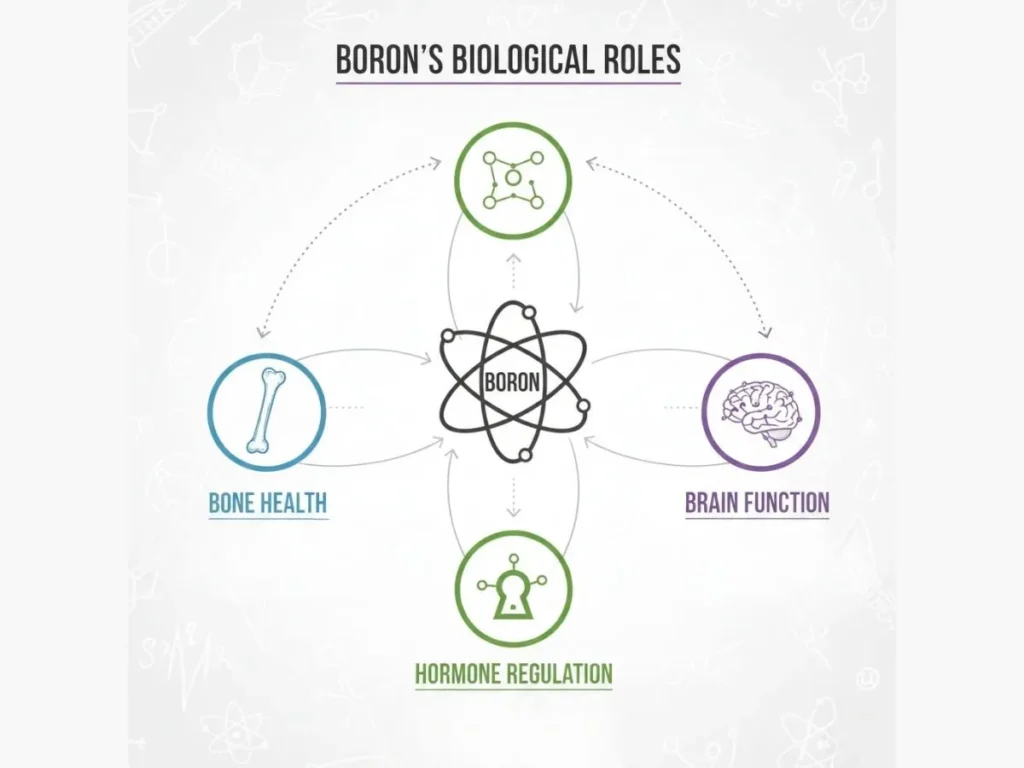
The Science of Boron and Its Biological Roles
Boron influences several physiological systems:
- Hormonal Regulation: Supports the conversion of total to free testosterone and enhances estrogen balance.
- Bone Metabolism: Increases calcium and magnesium retention, improving bone density.
- Cognitive Function: Supports neuronal signaling and brain cell membrane stability.
- Inflammation Control: Modulates enzymes involved in oxidative stress.
According to a 2015 Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology study, boron supplementation improved both bone and cognitive markers in postmenopausal women.
Signs and Health Effects of Boron Deficiency
Although true “deficiency” is rare, low boron intake has been associated with:
- Joint stiffness and poor bone density
- Brain fog and slower cognitive processing
- Hormonal imbalance (especially in men and women over 40)
- Reduced wound healing and higher inflammation levels
- Poor magnesium and calcium utilization
Because boron impacts multiple nutrient pathways, insufficient intake can mimic deficiencies in vitamin D, calcium, or magnesium — even when those nutrients are adequate.
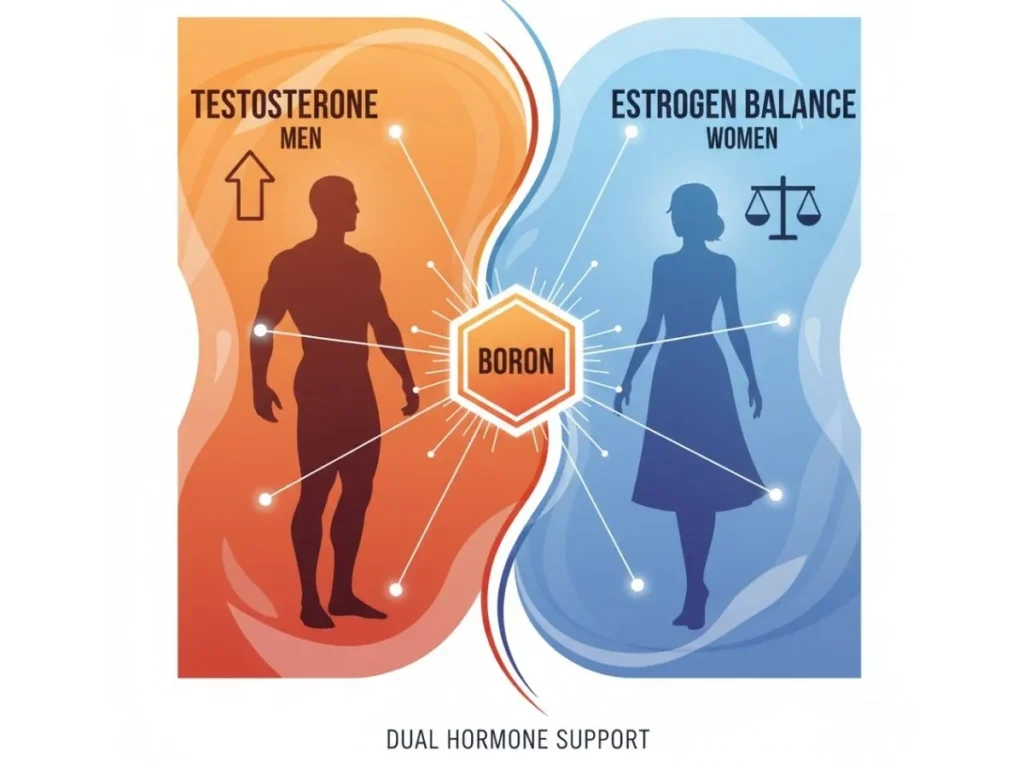
The Hidden Link Between Boron and Hormone Balance
Boron has a unique role in optimizing hormonal health. Studies show it increases free testosterone levels in men while also improving estrogen metabolism in women.
A 2011 study published in Environmental Health Perspectives found that 6 mg of boron daily increased free testosterone levels by 25% in just one week in healthy men.
For women, boron supports menstrual regularity and reduces PMS-related inflammation, acting as a mild natural adaptogen.
Boron’s Role in Bone Health, Brain Function, and Inflammation
1. Bone Health
Boron enhances the effects of vitamin D, magnesium, and calcium, the three foundational nutrients for bone density.
Low-boron diets correlate with increased fracture risk and reduced calcium absorption.
2. Cognitive and Neural Function
Boron helps stabilize neuron membranes, supporting clear thinking and short-term memory. Deficiency can impair fine motor coordination and alertness.
3. Inflammation and Pain Regulation
Boron has natural anti-inflammatory properties, reducing biomarkers like CRP (C-reactive protein). This may explain why populations with higher boron intake show fewer cases of arthritis and osteoarthritis.
Suggested image placement: A triple-panel infographic — bones, brain, and joints — showing boron’s influence on each system.
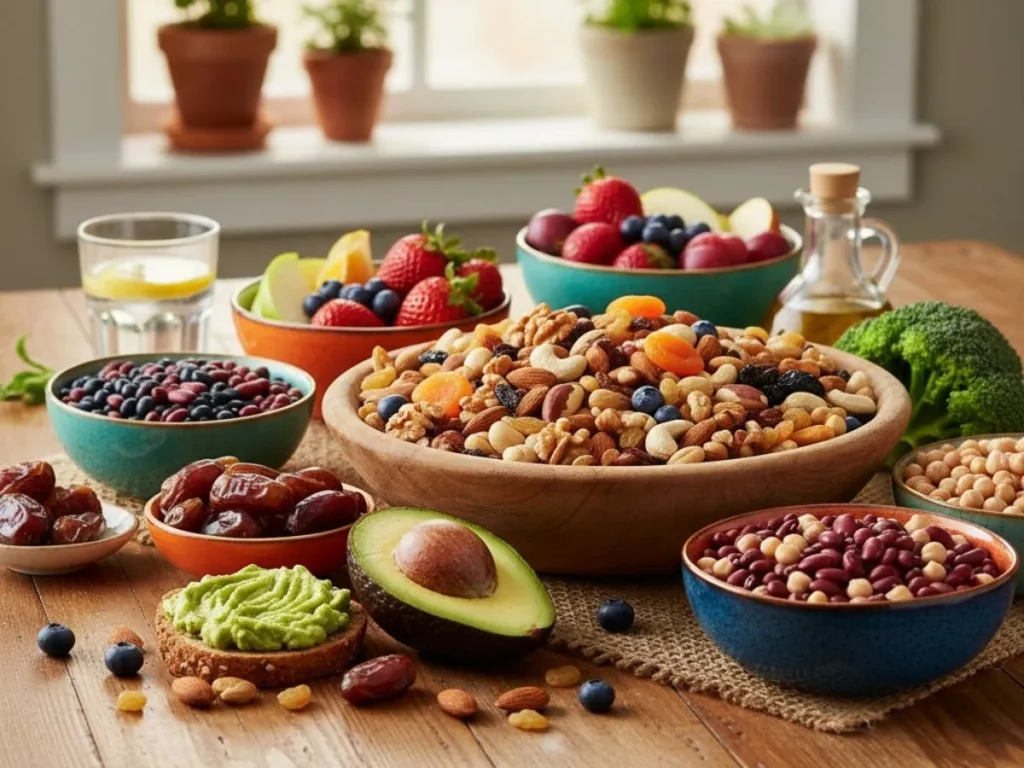
Dietary Sources of Boron
| Food Source | Serving Size | Boron (mg) |
|---|---|---|
| Avocado | 1 medium | 2.1 |
| Prunes | 5 pieces | 1.8 |
| Raisins | 1/4 cup | 1.2 |
| Almonds | 1 oz | 0.95 |
| Beans (various) | 1 cup cooked | 0.9 |
| Apple | 1 medium | 0.7 |
| Peanut butter | 2 tbsp | 0.4 |

Boron Supplementation: Dosage, Safety, and Timing
- Recommended dose: 3–6 mg per day for adults
- Best form: Boron citrate, glycinate, or chelated boron
- Timing: Once daily, ideally with a meal for better absorption
- Safety: Upper safe limit is 20 mg/day (per National Academies of Sciences)
Caution: Avoid high-dose, unverified boron supplements (>10 mg/day) for extended periods unless advised by a healthcare professional.
Checklist: How to Rebuild Optimal Boron Levels
✅ Include boron-rich foods like prunes, nuts, and avocados daily
✅ Choose unprocessed, mineral-rich plant foods over refined items
✅ Take 3–6 mg boron supplement if diet is low in natural sources
✅ Ensure adequate vitamin D, calcium, and magnesium intake
✅ Track hormonal balance and energy after 2–3 weeks
Expert Insights
“Boron may be the missing link between suboptimal bone density and hormonal imbalance in many adults. It’s small but mighty in its biological influence.”
— Dr. Megan Alvarez, Functional Medicine Specialist, California
“A diet rich in boron can naturally support testosterone and estrogen balance without pharmaceuticals, particularly beneficial for aging adults.”
— Dr. Ryan Cole, Integrative Nutritionist, Florida
Common Myths & FAQ
Q1: Can boron improve testosterone naturally?
Yes, studies show boron can increase free testosterone levels, but only within normal physiological ranges — not as a performance enhancer.
Q2: Is boron safe for daily use?
Absolutely. Doses under 10 mg/day are well-tolerated for long-term use.
Q3: Should women take boron supplements?
Yes, boron helps regulate estrogen metabolism and supports bone density in postmenopausal women.
Q4: Can I get enough boron from food alone?
If you eat a mostly processed or low-plant diet, supplementation may help bridge the gap.
Authoritative Resources
Other Interesting Articles on Fitoast
- Glycine Before Bed: The Amino Acid Hack for Deep Sleep & Recovery
- Sodium Myth Busting: The Right Way to Use Salt for Energy and Endurance
Conclusion & Call-to-Action
Boron might be the most underrated nutrient in modern nutrition. While the U.S. diet continues to drift toward refined foods and depleted soil crops, boron intake is quietly falling — taking bone, brain, and hormonal health along with it.
Reclaiming boron balance is simple: eat whole plant foods, ensure mineral diversity, and consider light supplementation. Small daily choices can restore a big piece of your long-term wellness puzzle.
Next Step: Add one boron-rich food to your daily diet and track your energy, focus, and joint comfort for a week — you’ll feel the difference that modern nutrition has forgotten.

